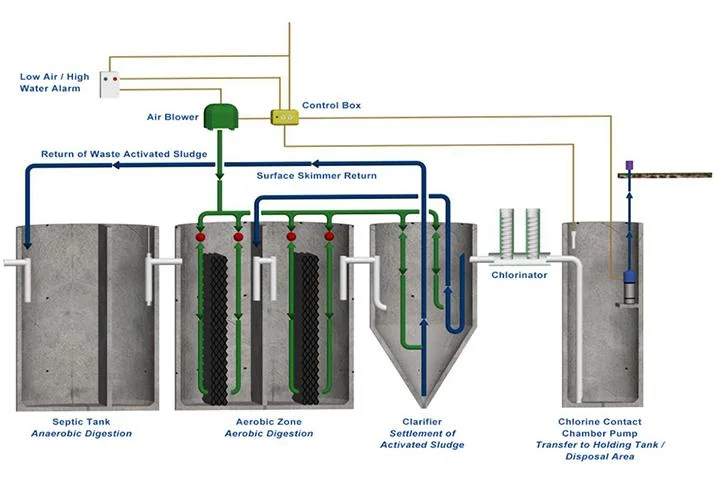
Water clarifiers are used to remove suspended solids from water, making it clearer and purer. Clarifiers work by gravity sedimentation, which means that the heavier suspended solids settle to the bottom of the tank while the lighter water rises to the top.
Clarifiers are used in a variety of water treatment applications, including:
- Municipal water treatment: Clarifiers are used to remove suspended solids from raw water before it is distributed to customers.
- Industrial wastewater treatment: Clarifiers are used to remove suspended solids from industrial wastewater before it is discharged into the environment.
- Food and beverage processing: Clarifiers are used to remove suspended solids from food and beverage products to improve their appearance and quality.
Filtration Systems
Water filtration systems are used to remove contaminants from water, making it safe to drink. Filtration systems work by passing the water through a porous material that traps the contaminants.
There are many different types of filtration systems, but some of the most common include:
- Sand filters: Sand filters are used to remove suspended solids, such as dirt and silt, from water.
- Carbon filters: Carbon filters are used to remove organic contaminants, such as chlorine and pesticides, from water.
- Reverse osmosis systems: Reverse osmosis systems are used to remove dissolved solids, such as salt and heavy metals, from water.
Filtration systems are used in a variety of water treatment applications, including:
- Municipal water treatment: Filtration systems are used to remove contaminants from raw water before it is distributed to customers.
- Point-of-use water treatment: Filtration systems are used to remove contaminants from water at the point of use, such as at a faucet or showerhead.
- Bottled water production: Filtration systems are used to remove contaminants from water before it is bottled and sold.
Pumping Stations
Water pumping stations are used to move water from one location to another. Pumping stations are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Water distribution: Pumping stations are used to distribute water from water treatment plants to homes and businesses.
- Wastewater treatment: Pumping stations are used to move wastewater from collection points to wastewater treatment plants.
- Irrigation: Pumping stations are used to move water from wells or rivers to irrigation systems.
Pumping stations can be very simple or very complex, depending on the application. Simple pumping stations may consist of a single pump, while complex pumping stations may consist of multiple pumps, motors, and other equipment.
Conclusion
Water clarifiers, filtration systems, and pumping stations are all essential components of water treatment and distribution systems. These systems work together to remove contaminants from water and deliver it to homes and businesses in a safe and reliable manner.
Automation in Municipal Water Treatment
Automation is playing an increasingly important role in municipal water treatment. Automated systems can help to improve the efficiency, quality, and safety of water treatment operations.
Here are some specific examples of how automation is being used in municipal water treatment:
- Chemical dosing: Automated systems can be used to dose chemicals into the water treatment process precisely and consistently. This helps to ensure that the water is treated properly and that the correct amount of chemicals is used.
- Process control: Automated systems can be used to control the various stages of the water treatment process, such as coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection. This helps to ensure that the water treatment process is running smoothly and that the water is meeting all quality standards.
- Monitoring: Automated systems can be used to monitor the water treatment process and collect data on water quality parameters such as temperature, pH, turbidity, and residual chlorine levels. This data can be used to identify and address potential problems early on.
- Alarm and notification: Automated systems can be used to set alarms and notifications for when water quality parameters exceed or fall below certain thresholds. This helps to ensure that operators are aware of any potential problems and can take corrective action promptly.
The use of automation in municipal water treatment offers a number of benefits, including:
- Improved efficiency: Automated systems can help to improve the efficiency of water treatment operations by automating repetitive tasks and freeing up operators to focus on more complex tasks.
- Improved quality: Automated systems can help to improve the quality of treated water by ensuring that chemicals are dosed precisely and consistently and that the water treatment process is running smoothly.
- Improved safety: Automated systems can help to improve the safety of water treatment operations by reducing the risk of human error and exposure to hazardous chemicals.
- Reduced costs: Automated systems can help to reduce the costs of water treatment operations by improving efficiency and reducing waste.
Here are some specific examples of automated systems that are being used in municipal water treatment:
- The Evoqua InSight Platform: The Evoqua InSight Platform is a cloud-based platform that provides real-time data on water quality and system performance. The platform can be used to monitor and control the water treatment process, identify and address potential problems early on, and optimize system performance.
- The GEA Water Intelligence Platform: The GEA Water Intelligence Platform is another cloud-based platform that provides real-time data on water quality and system performance. The platform can be used to monitor and control the water treatment process, identify and address potential problems early on, and optimize system performance.
- The Siemens Water Technology Simatic PCS 7: The Siemens Water Technology Simatic PCS 7 is a process control system that can be used to control the entire water treatment process, from raw water intake to treated water distribution. The system provides operators with a real-time view of the process and allows them to make adjustments as needed.
The use of automation in municipal water treatment is expected to grow in the coming years. As automation technology continues to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative and sophisticated automated solutions for the water treatment industry.
Automation in Point-of-use Water Treatment
Automation is also playing an increasingly important role in point-of-use (POU) water treatment. POU water treatment systems are installed at the point where water is used, such as at a kitchen faucet or showerhead. Automated POU water treatment systems can help to improve the quality, safety, and convenience of drinking water.
Here are some specific examples of how automation is being used in POU water treatment:
- Automatic valve control: Automated valves can be used to control the flow of water through the POU water treatment system. This helps to ensure that the water is treated properly and that the correct amount of water is used.
- Automatic filter backwash: Automated systems can be used to backwash the POU water treatment system’s filters on a regular basis. This helps to remove impurities from the filters and maintain the system’s performance.
- UV lamp monitoring: Automated systems can be used to monitor the UV lamp in the POU water treatment system. If the UV lamp fails, the system will automatically shut off to prevent untreated water from being dispensed.
- Leak detection and prevention: Automated systems can be used to detect and prevent leaks in the POU water treatment system. This helps to protect the system from damage and to prevent water waste.
The use of automation in POU water treatment offers a number of benefits, including:
- Improved water quality: Automated POU water treatment systems can help to improve the quality of drinking water by removing contaminants such as chlorine, sediment, and bacteria.
- Improved safety: Automated POU water treatment systems can help to improve the safety of drinking water by preventing the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms.
- Convenience: Automated POU water treatment systems are convenient to use, as they do not require any manual intervention to operate.
Here are some specific examples of automated POU water treatment systems:
- The Culligan Aqua-Cleer POU Water System: The Culligan Aqua-Cleer POU Water System is an automated POU water treatment system that uses reverse osmosis to remove contaminants from water. The system features an automatic valve control system, an automatic filter backwash system, and a UV lamp monitoring system.
- The GEA Water Intelligence HomeMaster POU Water System: The GEA Water Intelligence HomeMaster POU Water System is another automated POU water treatment system that uses reverse osmosis to remove contaminants from water. The system features an automatic valve control system, an automatic filter backwash system, and a UV lamp monitoring system.
- The 3M AquaPure POU Water System: The 3M AquaPure POU Water System is an automated POU water treatment system that uses a variety of technologies, including reverse osmosis, carbon filtration, and UV disinfection, to remove contaminants from water. The system features an automatic valve control system, an automatic filter backwash system, and a UV lamp monitoring system.
The use of automation in POU water treatment is expected to grow in the coming years. As automation technology continues to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative and sophisticated automated solutions for the POU water treatment market.
Automation in Bottled Water Production
Automation is playing an increasingly important role in bottled water production. Automated systems can help to improve the efficiency, quality, and safety of bottled water production operations.
Here are some specific examples of how automation is being used in bottled water production:
- Preform handling: Automated systems can be used to handle preforms, which are the plastic bottles before they have been blown and filled. This includes loading and unloading preforms from pallets, transporting them through the production line, and placing them in the blow molding machine.
- Blow molding: Automated blow molding machines can be used to blow preforms into bottles. These machines are capable of producing bottles at very high speeds and with great precision.
- Filling and capping: Automated filling and capping machines can be used to fill bottles with water and to cap them. These machines are also capable of producing bottles at very high speeds and with great precision.
- Inspection: Automated inspection systems can be used to inspect bottles for defects, such as cracks, scratches, and incorrect fill levels. These systems can also be used to reject defective bottles.
- Packaging: Automated packaging systems can be used to package bottles into cases or cartons. These systems are capable of packaging bottles at very high speeds and with great precision.
The use of automation in bottled water production offers a number of benefits, including:
- Improved efficiency: Automated systems can help to improve the efficiency of bottled water production operations by automating repetitive tasks and freeing up workers to focus on more complex tasks.
- Improved quality: Automated systems can help to improve the quality of bottled water by ensuring that bottles are filled and capped precisely and consistently. Automated inspection systems can also help to reduce the number of defective bottles that reach consumers.
- Improved safety: Automated systems can help to improve the safety of bottled water production operations by reducing the risk of human error and exposure to hazardous chemicals.
- Reduced costs: Automated systems can help to reduce the costs of bottled water production operations by improving efficiency and reducing waste.
Here are some specific examples of automated systems that are being used in bottled water production:
- The Krones Varioline: The Krones Varioline is a complete automated bottling line that can handle all aspects of bottled water production, from preform handling to packaging. The Varioline is capable of producing up to 150,000 bottles per hour.
- The Sidel Matrix Combi: The Sidel Matrix Combi is another complete automated bottling line that can handle all aspects of bottled water production. The Matrix Combi is capable of producing up to 160,000 bottles per hour.
- The GEA AquaPrima: The GEA AquaPrima is a modular automated bottling line that can be customized to meet the specific needs of bottled water producers. The AquaPrima is capable of producing up to 100,000 bottles per hour.
The use of automation in bottled water production is expected to grow in the coming years. As automation technology continues to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative and sophisticated automated solutions for the bottled water industry.
